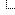PostgreSQL Basic Setup
Connect to PostgreSQL
To start using PostgreSQL, you need to connect to its prompt. Begin by switching to the postgres user:
sudo su postgres
Then, start PostgreSQL:
psql
Here, you can check the list of all available commands by typing \h. Alternatively, you can use \h followed by a command for which you need more information. To exit the whole environment, use \q.
Change User Password
By default, Linux will create a new postgres user whenever you install PostgreSQL. If you wish to modify the postgres user password, use the following command:
sudo passwd postgres
A prompt to enter the new password twice will appear. Next, switch to the PostgreSQL prompt and finish changing the password for the PostgreSQL postgres user:
su - postgres
If you receive an error, set a correct shell for the user with the command below:
su --shell /bin/bash postgres
Then, perform the same command:
su - postgres
Alternatively, it is also possible to change the user password from the PostgreSQL prompt. To do this, you'll need to first connect to the prompt:
sudo -u postgres psql
Then, to change the password, use the below command. Make sure to input your new password to replace NewPassw0rd:
ALTER USER postgres PASSWORD 'NewPassw0rd';
Lastly, restart the PostgreSQL service to enable these changes:
sudo service postgresql restart
Create a New User
The easiest way to create a new user is via interactive mode. First, switch to the postgres user:
su - postgres
Now, create a new user by entering the command below and choosing a name and user role:
createuser --interactive

To validate the new user, log in to PostgreSQL:
psql
From here, you can check all currently active users:
\du

Create a Database
Since you now have a user, all there is left to do is create a database with the createdb command.
Keep in mind that PostgreSQL assumes that the role name should be the same as the database name. Therefore, let's create a database with the same name as our user:
sudo -u postgres createdb newrole
To log in to the newly created database, you need to make a Linux user account under the same name:
sudo adduser newrole
Then, run the following command to connect:
sudo -u newrole psql
You can use \l or \list commands to show all databases. To identify your current database, type \c. In case you want more information about connections, such as the socket or port, use \conninfo.
The output of \conninfo command. It shows comprehensive information about connection to database.
Delete a Database
You can delete a database using the dropdb command with the following syntax:
dropdb yourdatabasename
Important! Remember to verify which database you are deleting, as this action is non-reversible.
Apart from the functions used in this article, PostgreSQL is very similar to other database management systems and has many familiar features:
- Table creation
- Table deletion
- Table updates
- Column addition
- Drop column
- Query table
- Alter commands
- Grant privileges
The syntax for these is similar to most other database management commands. For example, you can list all tables by using the \dt command. To list all roles, run the \du command.