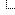How to Use wp_enqueue_style to Load CSS Stylesheets to WordPress
We’ll start with a few basic examples to help you better understand how the wp_enqueue_style() function works.
How to Enqueue Main style.css Stylesheet
To enqueue the main theme style.css stylesheet, use the wp_enqueue_style() function in your theme’s functions.php file.
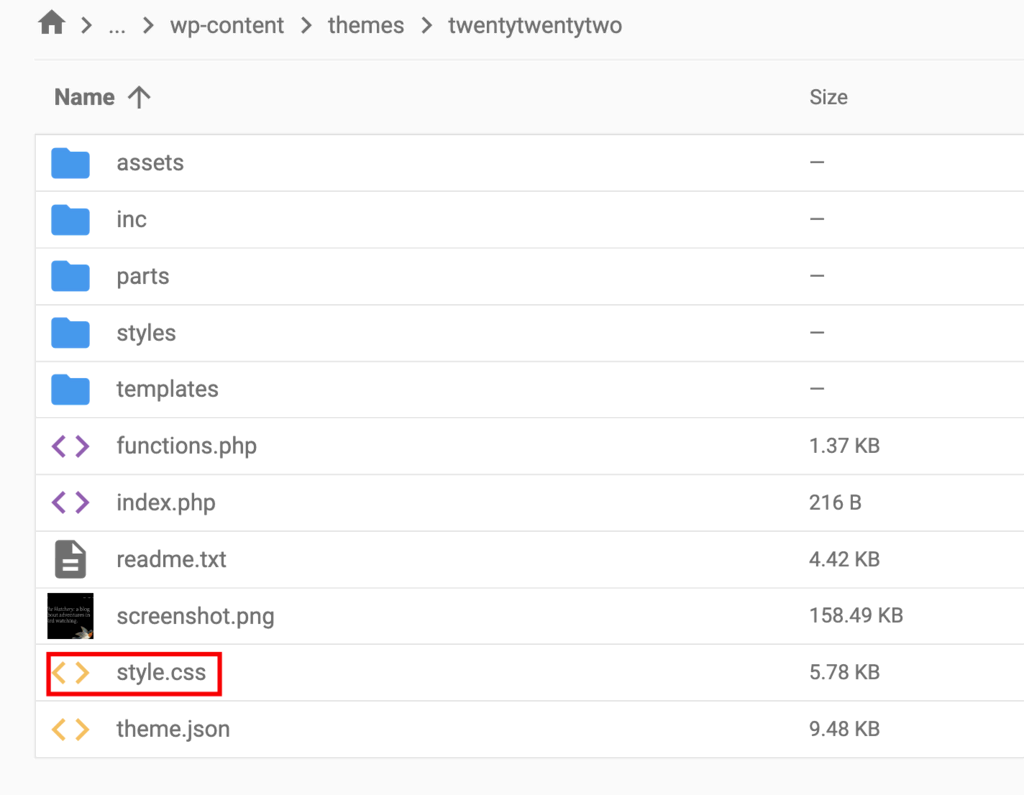
function my_theme_enqueue_styles() {
wp_enqueue_style('my_theme_style', get_stylesheet_uri());
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'my_theme_enqueue_styles');
In the code, my-theme-style is a unique name for the stylesheet you are enqueueing, while the get_stylesheet_uri() function handles the URL of the main theme’s style.css file.

Next, the wp_enqueue_style() function registers the style and adds it to the queue. Finally, the add_action() function adds your custom my_theme_enqueue_styles() function to the wp_enqueue_scripts hook, which will ensure that the stylesheet is enqueued properly.
How to Enqueue Other Stylesheets
You can also use the wp_enqueue_style() function to enqueue additional styles on top of the main stylesheet. For example, add extra styling options in a separate file.
function my_theme_enqueue_styles() {
wp_enqueue_style('my-theme-style', get_stylesheet_uri());
wp_enqueue_style('my-theme-extra-style', get_theme_file_uri('extra.css'));
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'my_theme_enqueue_styles');
In this method, we’ve used the get_theme_file_uri() function, which returns the file’s URL in the current theme’s directory. In our case, it’s extra.css. This way, the function will enqueue the main stylesheet first and then move to the additional styles.
How to Load External Stylesheets to WordPress
It’s possible to use the wp_enqueue_style() function to enqueue a stylesheet from an external source. The process can be beneficial if you want to use custom fonts or a stylesheet hosted on a content delivery network (CDN).
function theme_files() {
wp_enqueue_style('theme_custom', 'INSERT URL');
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'theme_files');
Remember to replace the INSERT URL part with an actual stylesheet URL.
How to Add Script Files to WordPress Using wp_enqueue_script
WordPress has a built-in function called wp_enqueue_script() that enables you to enqueue JavaScript or similar scripts. Add the following code to your theme’s functions.php file:
function theme_scripts() {
wp_enqueue_script('my-script', get_template_directory_uri() . '/js/my-script.js', array(), '1.0', true);
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'theme_scripts');
Note that this function uses more parameters:
my-script– the name of your script. You can choose any name you want./js/my-script.js– location of your script. In this case, it’s in thejsdirectory of the WordPress theme.array()– defines dependencies your script may have.1.0– the script version number.true– determines whether to load the script in the footer.
Useful Examples of wp_enqueue_style
Check out a few practical use cases of the wp_enqueue_style() function to improve your WordPress site.
Loading CSS Only on Specific Pages
Loading CSS on specific pages can provide several benefits for a WordPress website:
- Faster page load times – when you load CSS only on the pages where it is necessary, you avoid having unnecessary code. This will improve your overall site’s speed.
- Easier maintenance – you can change CSS files without affecting other pages.
add_action('init', 'register_custom_styles');
function register_custom_styles() {
wp_register_style('custom-design', '/wp-content/design.css');
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'conditionally_enqueue_styles_scripts');
function conditionally_enqueue_styles_scripts() {
if (is_page('contactus')) {
wp_enqueue_style('custom-design');
}
}
?>
Loading CSS File in the Footer
By moving CSS to the bottom of the page, the browser can prioritize loading the HTML and other important resources first. As a result, loading CSS in the footer improves your page load time.
function footer_style() {
wp_enqueue_style('custom-design', '/wp-content/design.css');
};
add_action('get_footer', 'footer_style');
?>
Remember that loading CSS in the footer can cause rendering issues and make the page look broken or unstyled. For this reason, load the most important CSS in the head section first, then move to the footer part.
Adding Dynamic Inline Styles
Dynamic inline styles allow you to add custom styles to individual elements on a web page. The easiest way to add inline styles is with the wp_add_inline_style() function, which loads them after a specific CSS file.
function theme_style() {
wp_enqueue_style('custom-style', get_template_directory_uri() . '/wp-content/design.css');
$bold_headlines = get_theme_mod('headline-font-weight');
$inline_style = '.headline { font-weight: ' . $bold_headlines . '; }';
wp_add_inline_style('custom-style', $inline_style);
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'theme_style');
?>
Keep in mind that inline style will only work after the design.css is properly enqueued.
Checking the Stylesheet’s Enqueue Status
Use the wp_style_is() function if you want more information about the stylesheet state. This function can check whether a CSS stylesheet file is in the queue, enqueued, registered, or ready to be displayed.
function check_styles() {
if (wp_style_is('main')) {
wp_enqueue_style('my-theme', '/custom-theme.css');
}
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'check_styles');
?>
Inserting Metadata into the Stylesheet
You can also use the wp_enqueue_style() function with the following code snippet to enqueue a CSS stylesheet with title metadata:
function theme_extra_styles() {
wp_enqueue_style('add-metadata', '/wp-content/design.css');
wp_style_add_data('add-metadata', 'title', 'My Awesome Title');
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'theme_extra_styles');
?>
In this example, we’ve used the wp_style_add_data() function and added a title to the CSS stylesheet.
Deregistering Style Files
It’s important to deregister CSS-style files you no longer use. When multiple plugins or themes enqueue the same style file, it can lead to conflicts and issues on the website.
function remove_default_stylesheet() {wp_dequeue_style('original-enqueue-stylesheet-handle');
wp_deregister_style('original-register-stylesheet-handle');
wp_register_style('new-style', get_stylesheet_directory_uri() . '/new.css', false, '1.0.0');
wp_enqueue_style('new-style');
}
?>