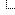Linux watch Command Examples
Check out some of the watch command use cases. Start by logging in to your virtual private server.
Highlighting Differences Between Updates
watch regularly updates the specified command’s output. To view the changing output, use the –d or –differences option, as it will highlight the changes:
watch -d freeHere, the RAM usage values are highlighted in the command line:

Changing Time Intervals
Users can effortlessly change the duration between outputs with the -n option followed by a digit representing the number of seconds. For example:
watch -n 5 dateThis command will reflect the updated date command output after every five seconds. Remember that Linux watch can’t observe regular intervals of less than 0.1 seconds.
Exiting After a Single Change
It’s often useful for the watch command to exit after one change in the output. Users can achieve this with the help of the –g option. An example would look like this:
watch -g free
Hiding the watch Command Header
It’s possible to turn off the header that shows a blank line, current time, command, and interval with the help of the –t option. For example:
watch -t free