How to Setup Databases and Users in MongoDB
Creating a New Database
MongoDB comes with a single database labeled admin. For testing purposes, it’s recommended to create a few additional databases. To do so, access the MongoDB shell:
mongosh
Once there, you can create a database using a single command. Keep in mind that, unlike SQL language, there is no separate command to create databases specifically.
MongoDB uses the same command for accessing and creating databases. If a database exists already, it can be used. Otherwise, the command will create it instead:
use [database_name]
In this tutorial, we will go with the customers database.
use customers
Creating a New User
By default, MongoDB does not include the default administrator account. Instead, different users for each database are needed. However, creating users with specific permissions in each database is necessary.
To create a new user, use the db.createUser() function. Specify the name, password, database, and roles it should have.
Similar to MongoDB, the db.createUser function receives parameters in JSON. So, to create a new user for the newly created database, run this command:
db.createUser(
{
user: "Hostinger",
pwd: "$tr0ngPa$$w0rD",
roles: [ { role: "userAdmin", db: "customers" } ]
}
)
There are several roles, including dbAdmin, dbUser, and readWrite, alongside many others. We recommend visiting the official MongoDB documentation to learn more.
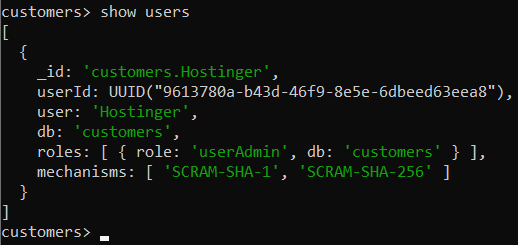
In order to show all created users, use this command:
show users
The output should look something like this on the terminal.
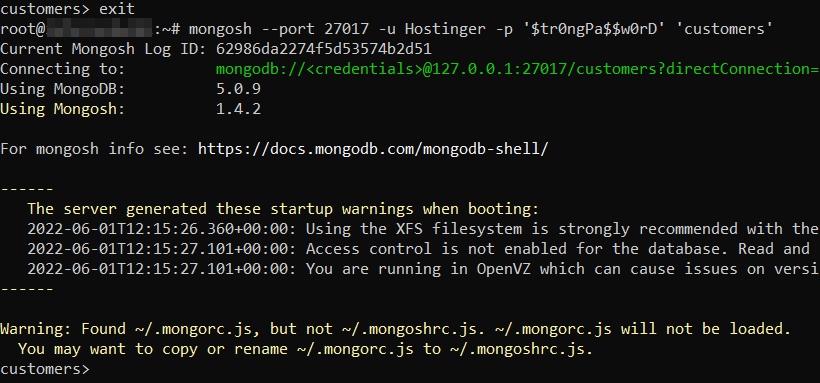
To test the operation, exit the MongoDB console with the exit command and run the following one to test the database connection:
mongosh --port [port] -u [username] -p '[password]' '[database]'
Enabling Remote Authentication
By default, MongoDB authorizes all logins from the local machine. This is not an issue if users are developing applications locally. However, you might encounter some problems when it’s time to deploy an application.
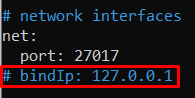
To avoid such issues in the future, open the /etc/mongodb.conf file and comment on the “bindIP: 127.0.0.1” line:
sudo nano /etc/mongodb.conf
Finally, restart the service:
sudo systemctl restart mongod
Now only local users will be able to log in without authentication.